Genetics x linked genes worksheet – Embark on an illuminating journey into the world of genetics and X-linked genes with our comprehensive worksheet. Delve into the intricacies of X-linked inheritance, unraveling the patterns and complexities that govern the transmission of genetic traits and disorders.
Our meticulously crafted worksheet provides a thorough understanding of the inheritance patterns associated with X-linked genes, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of genetic inheritance.
1. Introduction
Genetics is the study of genes, which are units of heredity that determine the characteristics of an organism. X-linked genes are genes located on the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes. In humans, females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
X-linked genes are responsible for a variety of traits and disorders. Some common X-linked traits include color blindness, hemophilia, and muscular dystrophy. X-linked disorders are typically more severe in males than in females, as males only have one copy of the X chromosome and therefore no backup copy of the gene.
2. Inheritance Patterns
The inheritance patterns for X-linked genes are different from those for autosomal genes, which are located on chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes. X-linked genes can be dominant or recessive.
- Dominant X-linked traitsare expressed in both males and females who carry the mutant allele. Males are more likely to be affected by dominant X-linked traits than females, as they only have one X chromosome and therefore no backup copy of the normal allele.
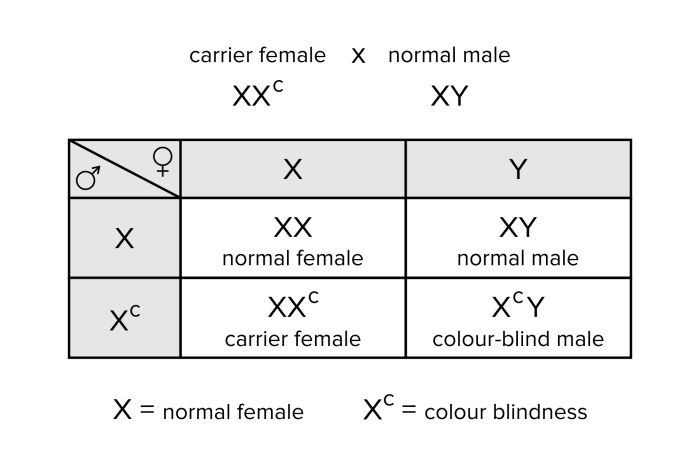
- Recessive X-linked traitsare only expressed in males who carry two copies of the mutant allele. Females who carry one copy of the mutant allele are called carriers and typically do not show any symptoms of the disorder. However, they can pass the mutant allele on to their children.
3. Genetic Testing

Genetic testing can be used to identify mutations in X-linked genes. This testing can be used to confirm a diagnosis of an X-linked disorder, to determine the carrier status of females, or to predict the risk of having a child with an X-linked disorder.
There are a variety of different methods that can be used for genetic testing of X-linked genes. These methods include:
- Karyotyping: This method involves staining and examining chromosomes to identify any abnormalities in their structure or number.
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH): This method uses fluorescent probes to identify specific genes or regions of chromosomes.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): This method is used to amplify specific regions of DNA, which can then be sequenced to identify mutations.
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS): This method is used to sequence large amounts of DNA quickly and inexpensively, which can identify mutations in multiple genes at once.
4. Case Studies: Genetics X Linked Genes Worksheet
There are a number of well-known case studies of individuals with X-linked genetic disorders. One example is the case of John Dalton, who was a famous English chemist and physicist who was born in 1766. Dalton was color blind, which is an X-linked recessive trait.
This means that he had two copies of the mutant allele for the gene that codes for color vision.
Another example is the case of the Romanov family, who were the last ruling family of Russia. The Romanov family had a history of hemophilia, which is an X-linked recessive disorder. The last tsar of Russia, Nicholas II, was a carrier of the hemophilia gene, and his son, Alexei, was affected by the disorder.
5. Counseling and Support
Genetic counselors play an important role in providing information and support to individuals and families affected by X-linked genetic disorders. Genetic counselors can help individuals and families to understand the inheritance patterns of X-linked disorders, the risks of having a child with an X-linked disorder, and the options for genetic testing and treatment.
Emotional and social support is also important for individuals and families affected by X-linked genetic disorders. There are a number of support groups and organizations that can provide information, resources, and support to individuals and families coping with these disorders.
Key Questions Answered
What are X-linked genes?
X-linked genes are genes located on the X chromosome. Males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes. This means that males are more likely to be affected by X-linked genetic disorders than females.
What are some examples of X-linked traits and disorders?
Some examples of X-linked traits include color blindness and hemophilia. Some examples of X-linked disorders include Duchenne muscular dystrophy and fragile X syndrome.
How are X-linked genes inherited?
X-linked genes are inherited in a dominant or recessive manner. Dominant X-linked traits are expressed in males who have one copy of the mutant gene and in females who have two copies of the mutant gene. Recessive X-linked traits are only expressed in males who have two copies of the mutant gene.