Consumers Try to Reduce Dissonance by Justifying Their Purchase Decision. Cognitive dissonance, a state of psychological discomfort caused by conflicting beliefs or actions, can arise after making a purchase. To alleviate this discomfort, consumers employ various strategies to justify their decisions, such as post-purchase rationalization and confirmation bias.
Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for marketers seeking to influence consumer behavior and enhance customer satisfaction.
This article delves into the concept of cognitive dissonance and its relevance to consumer behavior. It explores the ways in which consumers justify their purchase decisions to reduce dissonance, the role of post-purchase rationalization and confirmation bias in this process, and the implications for marketing strategies.
Additionally, it presents case studies and real-world examples that demonstrate how consumers reduce dissonance after making a purchase, and identifies potential areas for future research.
Cognitive Dissonance: Consumers Try To Reduce Dissonance By Justifying Their Purchase Decision.
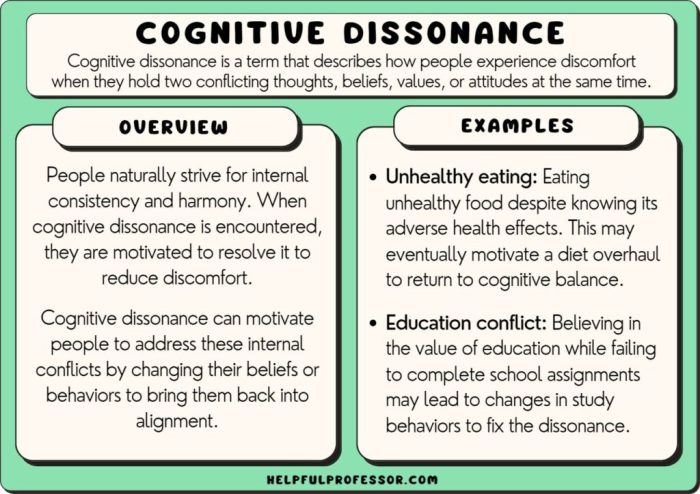
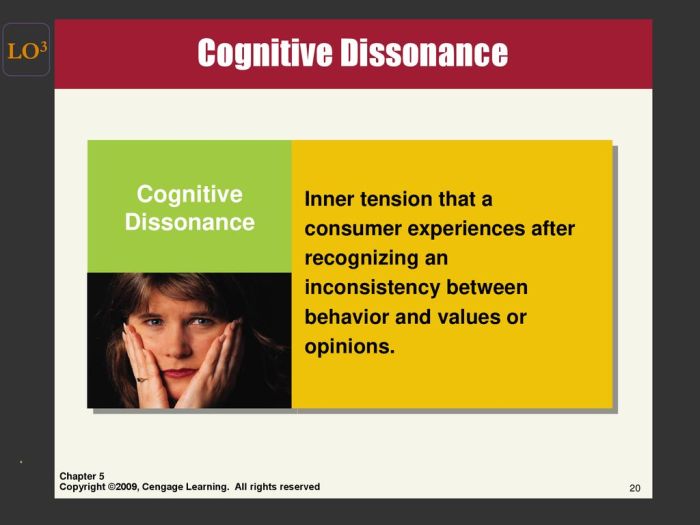
Cognitive dissonance is a psychological state of discomfort or tension that individuals experience when they hold two or more conflicting beliefs, values, or attitudes, or when their actions are not in line with their beliefs.
In the context of consumer behavior, cognitive dissonance arises when consumers make a purchase decision that conflicts with their existing beliefs or expectations. This discomfort can motivate consumers to seek ways to reduce the dissonance and restore cognitive balance.
Justification of Purchase Decisions, Consumers try to reduce dissonance by justifying their purchase decision.
Consumers employ various strategies to justify their purchase decisions and reduce cognitive dissonance. These include:
- Post-purchase rationalization:Consumers rationalize their purchase by focusing on the positive aspects of the product and downplaying any negative aspects.
- Confirmation bias:Consumers seek information that supports their purchase decision and avoid information that contradicts it.
- Selective perception:Consumers selectively perceive information that is consistent with their purchase decision and ignore information that is inconsistent.
Marketing Implications
Marketers can leverage the concept of cognitive dissonance to influence consumer behavior and increase customer satisfaction. Strategies include:
- Providing post-purchase support:By providing excellent customer service and support, marketers can help consumers reduce dissonance and increase satisfaction.
- Highlighting positive aspects:Marketers can emphasize the positive features and benefits of their products to reduce dissonance after purchase.
- Encouraging customer feedback:Encouraging customers to provide feedback can help marketers identify areas where they can improve their products or services and reduce dissonance.
Case Studies and Examples
Case studies and real-world examples demonstrate how consumers reduce dissonance after making a purchase:
- Starbucks:Starbucks customers often rationalize their high-priced coffee purchases by focusing on the premium quality and brand experience.
- Apple:Apple customers tend to exhibit confirmation bias by seeking out positive reviews and ignoring negative reviews of Apple products.
- Tesla:Tesla drivers often selectively perceive information that supports their decision to purchase an electric vehicle, such as environmental benefits and technological advancements.
Future Research Directions
Potential areas for future research on cognitive dissonance and consumer behavior include:
- The role of social media:How does social media influence consumers’ post-purchase evaluations and dissonance reduction strategies?
- The impact of personality traits:Do certain personality traits make consumers more or less susceptible to cognitive dissonance?
- Cross-cultural comparisons:How do cultural factors influence consumers’ experiences and strategies for reducing cognitive dissonance?
Query Resolution
What is cognitive dissonance?
Cognitive dissonance is a state of psychological discomfort experienced when an individual holds two or more conflicting beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors.
How do consumers justify their purchase decisions?
Consumers justify their purchase decisions through post-purchase rationalization, which involves emphasizing the positive aspects of the purchased product or service, and confirmation bias, which involves seeking information that supports their decision.
What are the implications of cognitive dissonance for marketers?
Cognitive dissonance can influence consumer behavior by affecting their product evaluations, purchase decisions, and post-purchase satisfaction. Marketers can leverage this understanding to develop strategies that address consumer concerns and reduce dissonance.